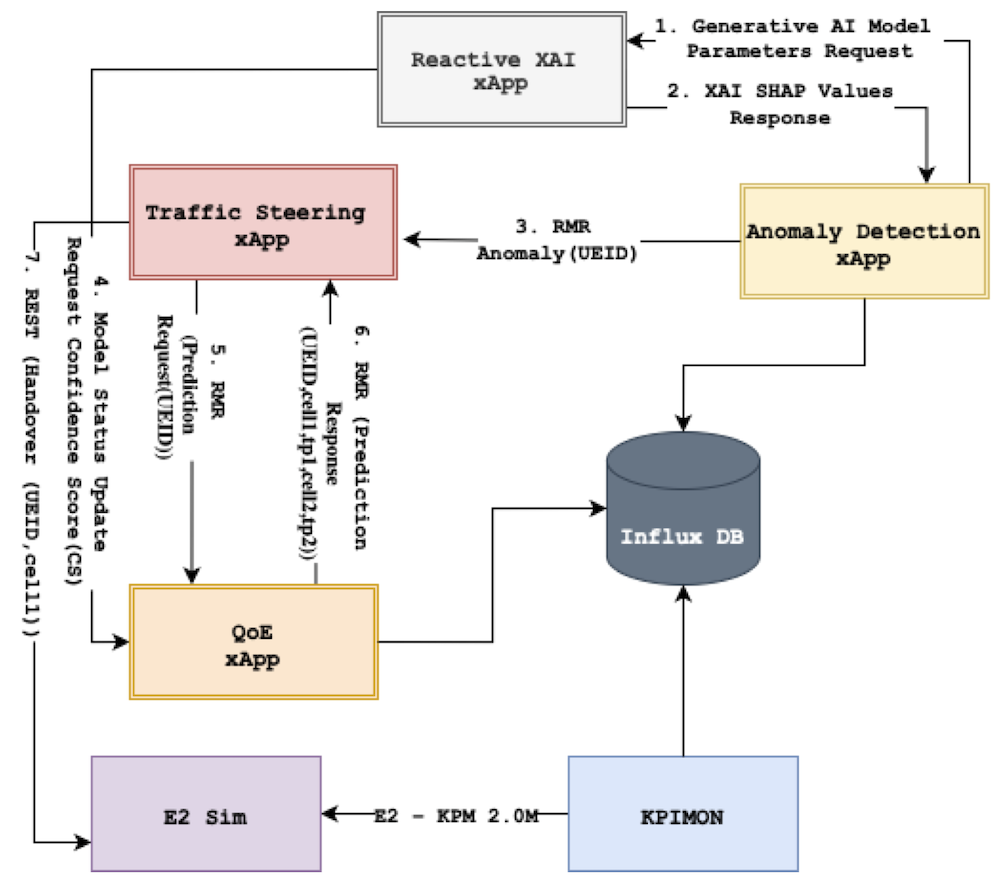
News and Announcements
- April 11, 2025

The TKN group presented three research talks at the 9th Workshop on Molecular Communications 2025. Sunasheer Bhattacharjee presented the idea of detecting exhaled breath biomarkers and their potential to identify human health anomalies through the lens of molecular communication. Saswati Pal introduced a machine learning-based approach for localizing infection sources in the cardiovascular system, showing that realistic physiological modeling improves accuracy and generalization. Lisa Y. Debus illustrated the importance of the experimental assessment of theoretical solutions with our evaluation of the influence of water, blood substitute, and blood as the background flow medium in magnetic nanoparticle-based molecular communication.
- April 03, 2025

The Telecommunication Networks Group (TKN) held its annual research retreat "CCS on Tour 2025" from April 1st to 4th. During the four-day event in Brodten (near Travemünde, Germany), we had interesting discussions on research topics like vehicular clouds, federated learning, raytracing, signal proagation models, simulation techniques. We also discussed best practices for research, best work-life optimization, meeting culture, and enjoyed social activities organized by the team.
- March 29, 2025
Our proposal Connecting in-body nano communication with body area networks (NaBoCom III) has been accepted for funding by the German research foundation DFG. In this project, we will investigate the integration of in-body nano networks with body are networks.
(link to more information)
- March 28, 2025

Our article Resilience in Edge Computing: Challenges and Concepts has been accepted for publication in Foundations and Trends in Networking.
Edge computing has evolved significantly from early research ideas to modern 5G mobile and multi-access edge computing (MEC). In many 6G-related projects, we see a clear trend toward virtualizing computing resources at the edge. Motivated by the cloud-edge-continuum that is the basis for next-generation metaverse applications, the need for low-latency solutions, distributed computing is now receiving even more attention. The last road blocker for the wide use of (virtualized) edge computing for mission-critical applications is resilience. In this context, resilience is the ability of modern communication and computation systems to deal with unknown and unforeseen events, both from internal and external sources. Thus, making MEC resilient to outages (e.g., system failures or energy outages due to natural disasters), security incidents (e.g., the use of intelligent jamming or malicious users), and overall challenging conditions (e.g., high mobility or impaired connectivity) is of the highest importance. In this article, we review the current state of the art of resilience in mobile edge computing. We explore MEC-specific challenges and resilience objectives, and discuss selected resilience measures. We trust that this article will be an invaluable resource for beginners and experts in the field as a compound resource on resilience in MEC.
(link to more information)
- March 27, 2025
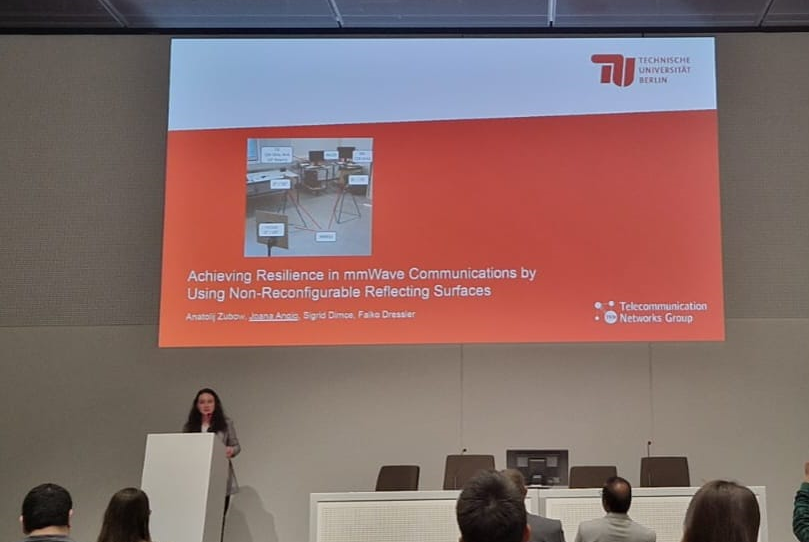

Joana Angjo presented our paper, Achieving Resilience in mmWave Communications by Using Non-reconfigurable Reflecting Surfaces at the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC 2025) in Milan, Italy. In this work, we show how non-reconfigurable reflecting surfaces (NRRSs) can be used towards improving resilience in mmWave communication. We build a testbed operating at 28 GHz and perform experiments that confirm that NRRSs boost communication reliability by constructing an artificial multipath environment, and they enable mmWave communication entirely via reflections.
(link to more information)
- March 27, 2025

Our article Stable Age of Information Scheduling with NOMA in Edge Networks has been accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Networking.
In this paper, we study a stable Age-of-Information (AoI) scheduling problem to handle the massive packet aggregation from arbitrary total of n end devices (sensor nodes) to an edge device via a single hop wireless channel when information constantly arrives at the end side. Specifically, we consider the arrivals of the information with an online injection mode, i.e., information is injected to end devices with an unknown injection rate in each time slot. After the information is injected, the AoI with respect to those end devices constantly increases until their fresh messages are received by the edge device, which characterizes the freshness of the information at destination. Based on the online injection mode, we propose the first distributed stable AoI scheduling algorithm combining NOMA (Non-Orthogonal Multiple-Access) technique in this paper, to minimize the expected average peak AoI (EAP-AoI) of our end-to-edge information system.
(link to more information)
- March 26, 2025

Our article How Mature is 5G Deployment? A Cross-Sectional, Year-Long Study of 5G Uplink Performance has been accepted for publication in Elsevier Computer Communications.
In this study, we aim to assess 5G deployment maturity via three conditions: (1) Does 5G performance remain stable over a long time span (1 year)? (2) Does 5G provide better performance than its predecessor Long-Term Evolution (LTE)? (3) Does the technology offer similar performance across diverse geographic areas and cellular operators? We answer this important question by conducting two year-long measurement campaigns of 5G uplink performance leveraging a custom Android app: one crowd-sourced, cross-sectional campaign spanning 8 major cities in 7 countries and two different continents (Europe and North America), and one controlled campaign focusing on mmWave deployment at a fixed location in the downtown area of Boston, MA. Our datasets show that 5G deployment in major cities appears to have matured, with no major performance improvements observed over a one-year period, but 5G does not provide consistent, superior measurable performance over LTE, especially in terms of latency, and further there exists clear uneven 5G performance across the 8 cities. Our study suggests that, while 5G deployment appears to have stagnated, it is short of delivering its promised performance and user experience gain over its predecessor.
(link to more information)
- March 24, 2025

Falko Dressler gave a keynote titled Cross-Technology Communication and Network Coding: A Great Team for Resilient Communication at IEEE WCNC International Workshop on Resilient 6G Networks (WResNet6G 2025), which was held in Milan, Italy.
(link to more information)
- March 18, 2025

We congratulate Isabel von Stebut for winning the Best Bachelor Thesis Award of the GI/ITG Communication and Distributed Systems (KuVS) special interest group! The prize will be awarded at NetSys 2025. Isabel's thesis has already lead to a publications at IEEE PIMRC 2024 (ResCTC: Resilience in Wireless Networks through Cross-Technology Communication).
- March 18, 2025

We congratulate Lisa Y. Debus for winning the Best Master Thesis Award of the GI/ITG Communication and Distributed Systems (KuVS) special interest group! The prize will be awarded at NetSys 2025. Lisa's thesis has already lead to two publications at IEEE GLOBECOM 2023 (Reinforcement Learning-based Receiver for Molecular Communication with Mobility) and a follow-up journal paper published in IEEE Trans. on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communication (Synchronized Relaying in Molecular Communication: An AI-based Approach using a Mobile Testbed Setup).